The latest RAC Foundation 'state of the nation' bridges survey has recorded the lowest proportion of substandard bridges since the poll began in 2016.
One in every 25 council-maintained road bridges in Great Britain is officially deemed as ‘substandard’ – defined as being unable to carry the largest 44-tonne lorries allowed on the nation’s roads.
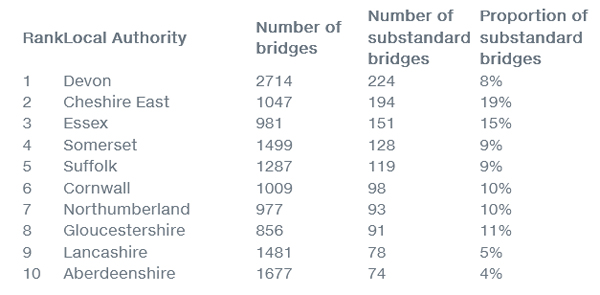
The 10 councils in Britain with the highest number of substandard bridges
The latest results are based on Freedom of Information responses from 201 of the total 208 local highway authorities in England, Scotland and Wales.
Between them, these councils are responsible for 73,208 road bridges, of which 2,928 are substandard – representing 4% of the total.
In last year’s survey, 3,174 bridges (4.4% of the 72,540 total) were classed as substandard. This was based on responses from 200 councils out of 207. The figures were slightly amended after last year’s initial announcement due to subsequent responses being added in.
The proportion of substandard bridges has remained fairly constant since the survey started eight years ago period. The second lowest proportion was 4.27% in 2018-19 and the highest was 4.6% in 2016-17.
Based on responses from 122 councils (61% of the 201 total), it would cost £4.1bn to clear the total backlog of maintenance work on the 45,796 bridges (63% of the 73,208 total) they manage between them.
Extrapolating from this figure, the RAC Foundation estimated that the total outstanding value of the bridge maintenance work for highways authorities in Great Britain is around £6.8bn. Last year’s survey saw the 196 councils who initially responded, who had responsibility for maintaining 71,925 bridges, report a total maintenance backlog of £5.861bn. Budget limitations mean councils anticipate that only 292 substandard bridges will be brought back up to full carrying capacity within the next five years.
The RAC Foundation also asked councils about what ‘specific issues concerned them most when it came to managing their bridge stocks’.
The responses were broadly categorised as follows:
- weather and climate change impacts
- budgetary pressures
- inflationary effects
- staffing, including lack of trained personnel, recruitment and retention
- skills outside of councils, particularly among contractors and consultants
- ageing infrastructure
- specific issues relating to bridges under/over railways, or liaison with Network Rail.
The RAC Foundation highlighted that ‘increasing concern about weather and climate impacts was particularly notable this year’. This included the problem of ground shrinkage caused by hotter, drier weather, as well as more typical issues such as the heavier rainfall potentially causing flooding, washout and the increased scouring of submerged parts of a structure.
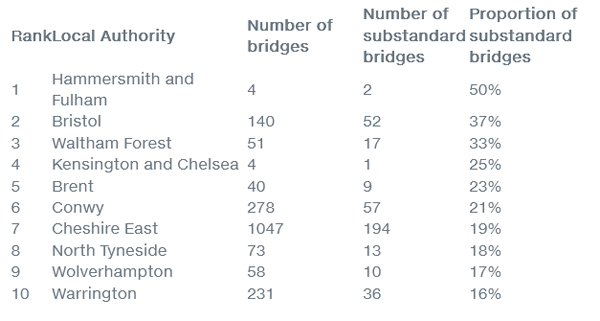
The 10 councils in Britain with the highest proportion of substandard bridges
RAC Foundation director Steve Gooding said: ‘While on the one hand it looks like councils are holding their own in keeping their road networks functioning, with every year which passes we are seeing the challenge of maintaining climate resilience increase in the face of more extreme weather.
‘It is unrealistic to think that there will be vastly more money added to the road and bridge maintenance pot but there are measures that could help stem the tide of decline, such as a real drive to recruit, train and retain engineers with the right expertise, plus the delivery of a fresh five-year funding settlement for local roads, which would at least allow highway teams to plan ahead.
‘Ideally, faced with the long-term challenge of constrained funding and deteriorating weather we desperately need innovative engineering solutions to provide cheaper, more resilient repairs. The real danger lies in the change in climate – more temperature extremes and more wind, rain, snow and ice are putting an ever-greater strain on the foundations of our roads and the structures that carry them.’
The study was carried out with the help of the National Bridges Group of ADEPT, which noted that the UK bridge stock represents centuries of investment. And so with many UK bridges were built decades and even centuries ago, the designers could not have envisaged the type, size and volume of traffic seen today.
Keith Harwood, chair of ADEPT National Bridges Group, said: ‘As our bridges age and face mounting pressures from increased traffic and the impacts of climate change, maintaining their resilience becomes increasingly critical.
‘Through insightful statistics, this report demonstrates - the financial constraints, staffing and skills shortages, and environmental factors confronting our ageing infrastructure.
‘The ADEPT National Bridges Group extends its gratitude to the RAC Foundation for their ongoing dedication to compiling such valuable data, which highlights the evolving trends and concerns of Bridge Managers nationwide.’
The definition of a ‘road bridge’ in the Well-managed Highway Infrastructure code of practice is a ‘structure with a span of 1.5m or more providing public highway passage for motor vehicles over an obstacle such as a watercourse, railway, road or valley’.